The easiest way to get started learning Heron is to install and run pre-compiled Heron binaries, which are currently available for:
- Mac OS X
- Ubuntu >= 14.04
For other platforms, you need to build from source. Please refer to Heron Developers.
Step 1 — Download Heron binaries using installation scripts
Go to the releases page for Heron and download two installation scripts for your platform. The names of the scripts have this form:
heron-client-install-0.14.7-PLATFORM.shheron-tools-install-0.14.7-PLATFORM.sh
The installation scripts for Mac OS X (darwin), for example, would be named
heron-client-install-0.14.7-darwin.sh and
heron-tools-install-0.14.7-darwin.sh.
Once you’ve downloaded the scripts, run the Heron client script with the
--user flag set:
$ chmod +x heron-client-install-VERSION-PLATFORM.sh
$ ./heron-client-install-VERSION-PLATFORM.sh --user
Heron client installer
----------------------
Uncompressing......
Heron is now installed!
Make sure you have "${HOME}/bin" in your path.
...
To add ~/bin to your path, run:
$ export PATH=$PATH:~/bin
Now run the script for Heron tools (setting the --user flag):
$ chmod +x heron-tools-install-VERSION-PLATFORM.sh
$ ./heron-tools-install-VERSION-PLATFORM.sh --user
Heron tools installer
---------------------
Uncompressing......
Heron Tools is now installed!
...
To check Heron is successfully installed, run:
$ heron version
heron.build.version : {#{#HUGOSHORTCODE-5#}#}
heron.build.time : Sat Aug 6 12:35:47 PDT 2016
heron.build.timestamp : 1470512147000
heron.build.host : ${HOSTNAME}
heron.build.user : ${USERNAME}
heron.build.git.revision : 26bb4096130a05f9799510bbce6c37a69a7342ef
heron.build.git.status : Clean
Step 2 — Launch an example topology
If you set the --user flag when running the installation scripts, some example
topologies will be installed in your ~/.heron/examples directory. You can
launch an example topology locally (on your machine)
using the Heron CLI tool:
# Submit ExclamationTopology locally in deactivated mode.
$ heron submit local \
~/.heron/examples/heron-examples.jar \
com.twitter.heron.examples.ExclamationTopology \
ExclamationTopology \
--deploy-deactivated
INFO: Launching topology 'ExclamationTopology'
...
[2016-06-07 16:44:07 -0700] com.twitter.heron.scheduler.local.LocalLauncher INFO: \
For checking the status and logs of the topology, use the working directory \
$HOME/.herondata/topologies/local/${ROLE}/ExclamationTopology # working directory
INFO: Topology 'ExclamationTopology' launched successfully
INFO: Elapsed time: 3.409s.
This will submit the topology to your locally running Heron cluster but it won’t activate the topology. That will be explored in step 5 below.
Note the output shows if the topology has been launched successfully and the working directory.
To check what’s under the working directory, run:
$ ls -al ~/.herondata/topologies/local/${ROLE}/ExclamationTopology
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 2299 Jun 7 16:44 ExclamationTopology.defn
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5 Jun 7 16:44 container_1_exclaim1_1.pid
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5 Jun 7 16:44 container_1_word_2.pid
drwxr-xr-x 11 username role 374 Jun 7 16:44 heron-conf
drwxr-xr-x 4 username role 136 Dec 31 1969 heron-core
-rwxr-xr-x 1 username role 2182564 Dec 31 1969 heron-examples.jar
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5 Jun 7 16:44 heron-executor-0.pid
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 0 Jun 6 13:33 heron-executor.stderr
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 17775 Jun 7 16:44 heron-executor.stdout
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5 Jun 7 16:44 heron-shell-0.pid
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5 Jun 7 16:44 heron-tmaster.pid
drwxr-xr-x 25 username role 850 Jun 7 16:44 log-files
-r--r--r-- 1 username role 4506 Jun 8 12:05 metrics.json.metricsmgr-0.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5 Jun 7 16:44 metricsmgr-0.pid
-r-xr-xr-x 1 username role 279 Dec 31 1969 release.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5 Jun 7 16:44 stmgr-1.pid
All instances’ log files can be found in log-files under the working directory:
$ ls -al ~/.herondata/topologies/local/${ROLE}/ExclamationTopology/log-files
total 1018440
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 94145427 Jun 8 12:06 container_1_exclaim1_1.log.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 75675435 Jun 7 16:44 container_1_word_2.log.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 187401024 Jun 8 12:06 gc.container_1_exclaim1_1.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 136318451 Jun 8 12:06 gc.container_1_word_2.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 11039 Jun 8 11:16 gc.metricsmgr.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 300 Jun 7 16:44 heron-shell.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 29631 Jun 7 16:44 heron-ExclamationTopology-scheduler.log.0
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 2382215 Jun 7 15:16 heron-stmgr-stmgr-1.username.log.INFO
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 5976 Jun 7 16:44 heron-tmaster-ExclamationTopology2da9ee6b-c919-4e59-8cb0-20a865f6fd7e.username.log.INFO
-rw-r--r-- 1 username role 12023368 Jun 8 12:06 metricsmgr-0.log.0
Step 3 — Start Heron Tracker
The Heron Tracker is a web service that
continuously gathers information about your Heron cluster. You can launch the
tracker by running the heron-tracker command (which is already installed):
$ heron-tracker
... Running on port: 8888
... Using config file: $HOME/.herontools/conf/heron_tracker.yaml
You can reach Heron Tracker in your browser at http://localhost:8888
and see something like the following upon successful submission of the topology:
![]()
To explore Heron Tracker, please refer to Heron Tracker Rest API
Step 4 — Start Heron UI
Heron UI is a user interface that uses Heron Tracker to provide detailed visual representations of your Heron topologies. To launch Heron UI:
$ heron-ui
... Running on port: 8889
... Using tracker url: http://localhost:8888
You can open Heron UI in your browser at http://localhost:8889
and see something like this upon successful submission of the topology:
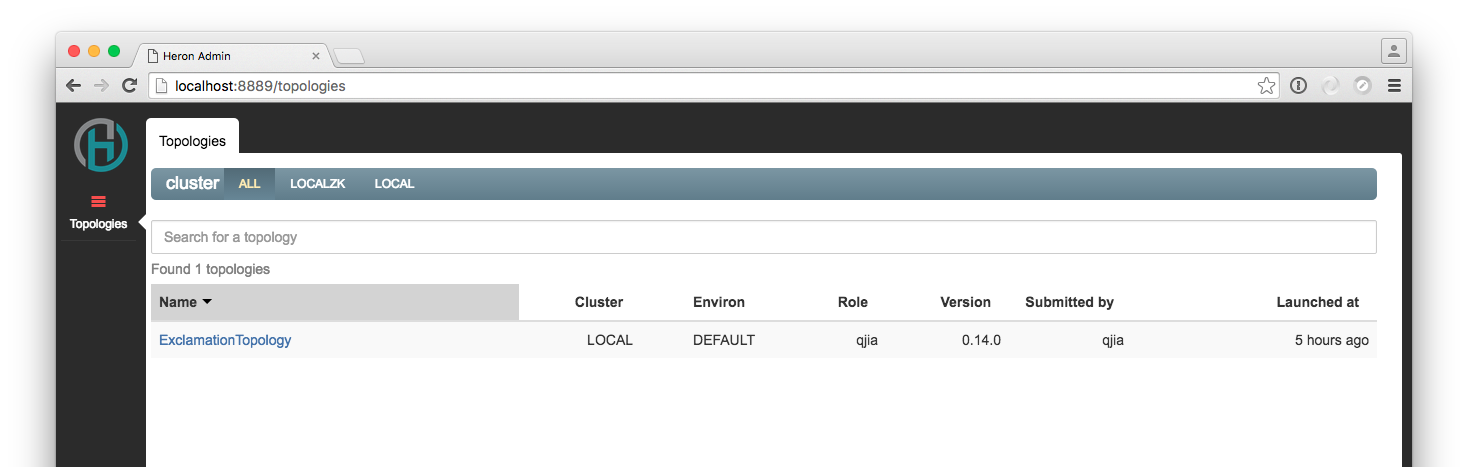
To play with Heron UI, please refer to Heron UI Usage Guide
Step 5 — Explore topology management commands
In step 2 you submitted a topology to your local cluster. The heron CLI tool
also enables you to activate, deactivate, and kill topologies and more.
$ heron activate local ExclamationTopology
$ heron deactivate local ExclamationTopology
$ heron kill local ExclamationTopology
Upon successful actions, a message similar to the following will appear:
INFO: Successfully activated topology 'ExclamationTopology'
INFO: Elapsed time: 1.980s.
For more info on these commands, read about topology lifecycles.
To list the available CLI commands, run heron by itself:
usage: heron <command> <options> ...
Available commands:
activate Activate a topology
deactivate Deactivate a topology
help Prints help for commands
kill Kill a topology
restart Restart a topology
submit Submit a topology
version Print version of heron-cli
For detailed documentation, go to http://heronstreaming.io
To invoke help output for a command, run heron help COMMAND. Here’s an
example:
$ heron help submit
usage: heron submit [options] cluster/[role]/[environ] topology-file-name topology-class-name [topology-args]
Required arguments:
cluster/[role]/[env] Cluster, role, and environ to run topology
topology-file-name Topology jar/tar/zip file
topology-class-name Topology class name
Optional arguments:
--config-path (a string; path to cluster config; default: "$HOME/.heron/conf")
--config-property (key=value; a config key and its value; default: [])
--deploy-deactivated (a boolean; default: "false")
-D DEFINE Define a system property to pass to java -D when
running main.
--verbose (a boolean; default: "false")
Step 6 — Explore other example topologies
The source code for the example topologies can be found on GitHub. The included example topologies:
AckingTopology.java— A topology with acking enabled.ComponentJVMOptionsTopology.java— A topology that supplies JVM options for each component.CustomGroupingTopology.java— A topology that implements custom grouping.ExclamationTopology.java— A spout that emits random words to a bolt that then adds an exclamation mark.MultiSpoutExclamationTopology.java— a topology with multiple spouts.MultiStageAckingTopology.java— A three-stage topology. A spout emits to a bolt that then feeds to another bolt.TaskHookTopology.java— A topology that uses a task hook to subscribe to event notifications.
Troubleshooting
In case of any issues, please refer to Quick Start Troubleshooting.
Next Steps
- Upgrade Storm topologies with simple
pom.xmlchanges - Deploy topologies in clustered, scheduler-driven environments (such as on Aurora and locally)
- Develop topologies for Heron